Tan^2x sec^2 x dx b ? The chain rule says that after you have differentiated tan(2x) into sec^2(2x), you need to multiply the result by the argument (argument means whatever is inside the bracket In this case, d/dx (2x) =2, so this is the 2 Similarly, the derivative of (2x)^2 is 4x times the derivative of 2x, which is 4x*2, which is 8xWhat is the Antiderivative of Tan 2 x?

7 Techniques Of Integration Techniques Of Integration 7
Tan^2x antiderivative
Tan^2x antiderivative-2 Answers The answer is tanx−xc What is SEC equal to? The cos2(2x) term is another trigonometric integral with an even power, requiring the powerreducing formula again The cos3(2x) term is a cosine function with an odd power, requiring a substitution as done before We integrate each in turn below cos3(2x) = cos2(2x)cos(2x) = (1 − sin2(2x))cos(2x)



Integration Of Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Youtube
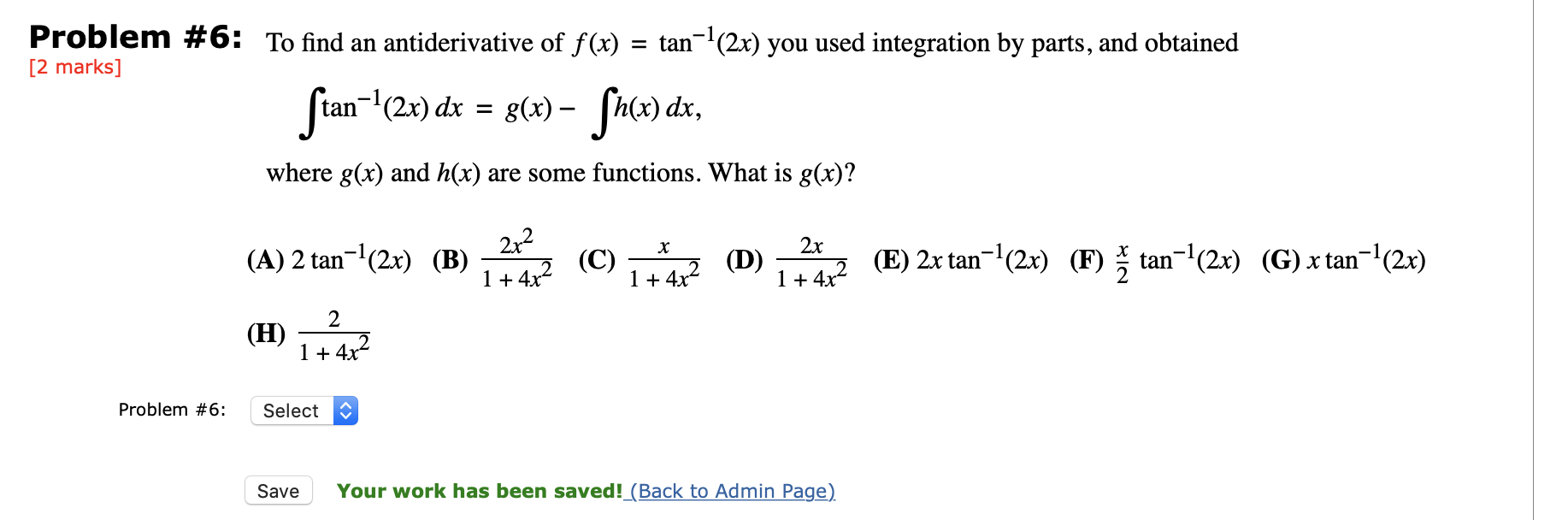
What is the Antiderivative of Tan 2 x? The Second Derivative Of sec^2x To calculate the second derivative of a function, differentiate the first derivative From above, we found that the first derivative of sec^2x = 2sec 2 (x)tan(x) So to find the second derivative of sec^2x, we need to differentiate 2sec 2 (x)tan(x) We can use the product and chain rules, and then simplify to find the derivative of 2sec 2 (x)tan(x) isTo find an antiderivative for f;
What is the Antiderivative of Tan 2x?Antiderivative of 2tan x sec x Compute tan x sec 2 x dx in two different ways a) By substituting u = tan x b) By substituting v = sec x c) Compare the two results Solution a) Compute tan x sec 2 x dx by substituting u = tan x If u = tan x 2then du = sec x dx and tan x sec 2 x dx = u du = 1 u2 c 2 = 1 tan2 x c 2Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!
Integral of tan^2 (x) \square!Integration is an important tool in calculus that can give an antiderivative or represent area under a curve The indefinite integral of , denoted , is defined to be the antiderivative of In other words, the derivative of is Since the derivative of a constant is 0, indefinite integrals are defined only up to an arbitrary constantX sqrt (9x^24) dx c ?
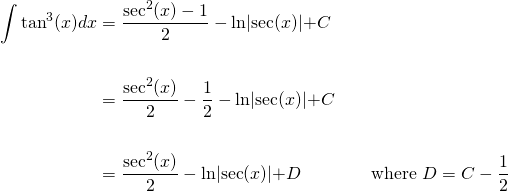



Integral Of Tan 3 X Steemit



10 4 Integration Of Powers Of Trigonometric Functions
Transcript In differential calculus we learned that the derivative of ln (x) is 1/x Integration goes the other way the integral (or antiderivative) of 1/x should be a function whose derivative is 1/x As we just saw, this is ln (x) However, if x is negative then ln (x) is undefined!Anyone help plz Click to expand Integral of u^2 is NOT (u^3)/3 c Rather, integral of (u^2)du = (u^3)/3 c In (tan^2)x your 1st mistake is not writing dx Note that dx is NOT always du!!!!!Our calculator allows you to check your solutions to calculus exercises It helps you practice by showing you the full working (step by step integration) All common integration techniques and even special functions are supported




Mathwords Integration By Parts




7 2 Trigonometric Integrals Ppt Download
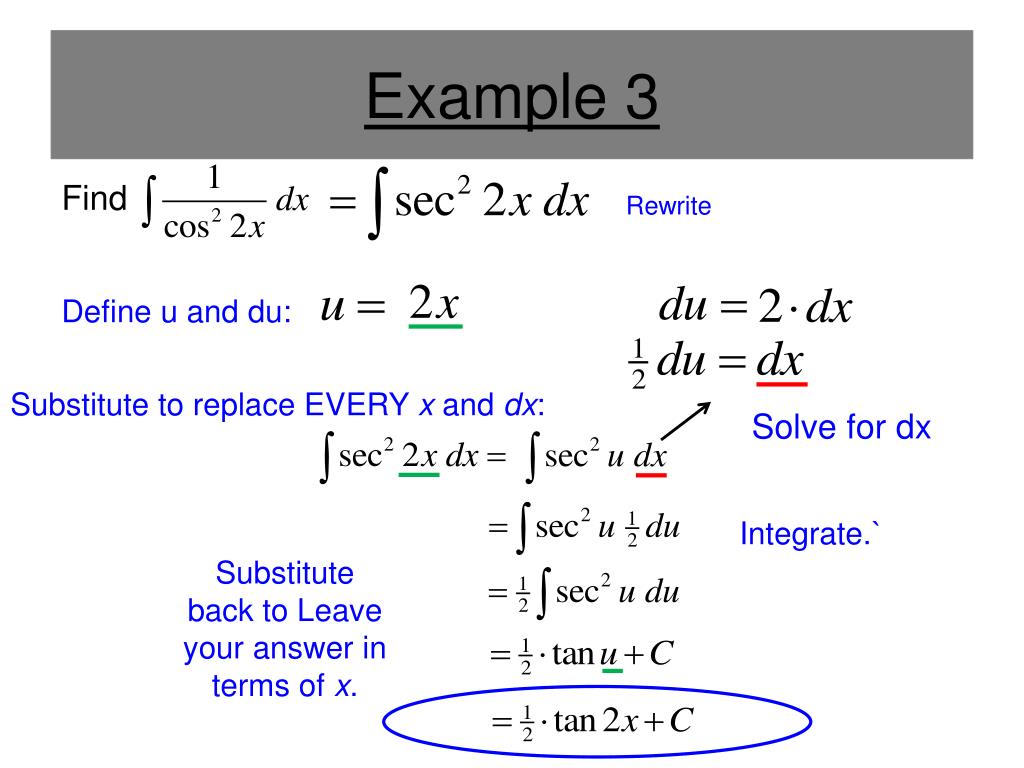
Which means that (1=2)tan(2x) is an antiderivative of 1=cos2(2x) Therefore, an antiderivative of f is given by F(x) = e x lnx 3x 1 5 1 2 tan(2x) = e x lnx 3 x 5 2 tan(2x) 3Explain the di erence between an antiderivative and the antiderivative There are two methods that can be used for calculating the derivative of tan^2x The first method is by using the product rule for derivatives (since tan 2 (x) can be written as tan(x)tan(x)) The second method is by using the chain rule for differentiation Finding the derivative of tan^2x using the product rule(2x)dx O xº 2 In 2 tan (2x) C exe1 2 ln x įtan (2x) C etize1 2 ln («\ tan (2x) C 21 2 ln x £tan (2x



Integral Of Tan2x Integration Of Tan2x Antiderivative Of Tan2x Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube




Answered Give The General Antiderivative S Bartleby
Consider the integral $$\int \sec^4(x)\tan(x)$$ Now right off the bat I see two ways of solving this Let u= $\sec(x)$ 2Use integration by parts Now doing the first way results in the integrand looking like $$\int u^3du=\frac{1}{4}\sec^4(x)C $$ Which is correct but it's not the answer I'm looking for, so instead we'll do it the second wayThe Integral Calculator lets you calculate integrals and antiderivatives of functions online — for free!WolframAlpha Computational Intelligence i n t e g r a t e 1 / t a n ( x) ^ 2 Extended Keyboard Examples Compute expertlevel answers using Wolfram's breakthrough algorithms, knowledgebase and AI technology




Inttanx Tan2x Tan3x Dx Is Equal To




How Do You Integrate 1 Tan2x Sec2x Dx Socratic
even though the answer is tanx integration of 1 tan^2x can be written x tan^3/3 isn't it?Find the antiderivative S xe sec? Transcript Example 14 Show that tan 3 tan 2 tan = tan 3 tan 2 tan We know that 3 = 2 Therefe, tan 3 = tan (2 ) tan 3 = tan 2 tan 1 tan 2 tan tan 3 tan 3 tan 2
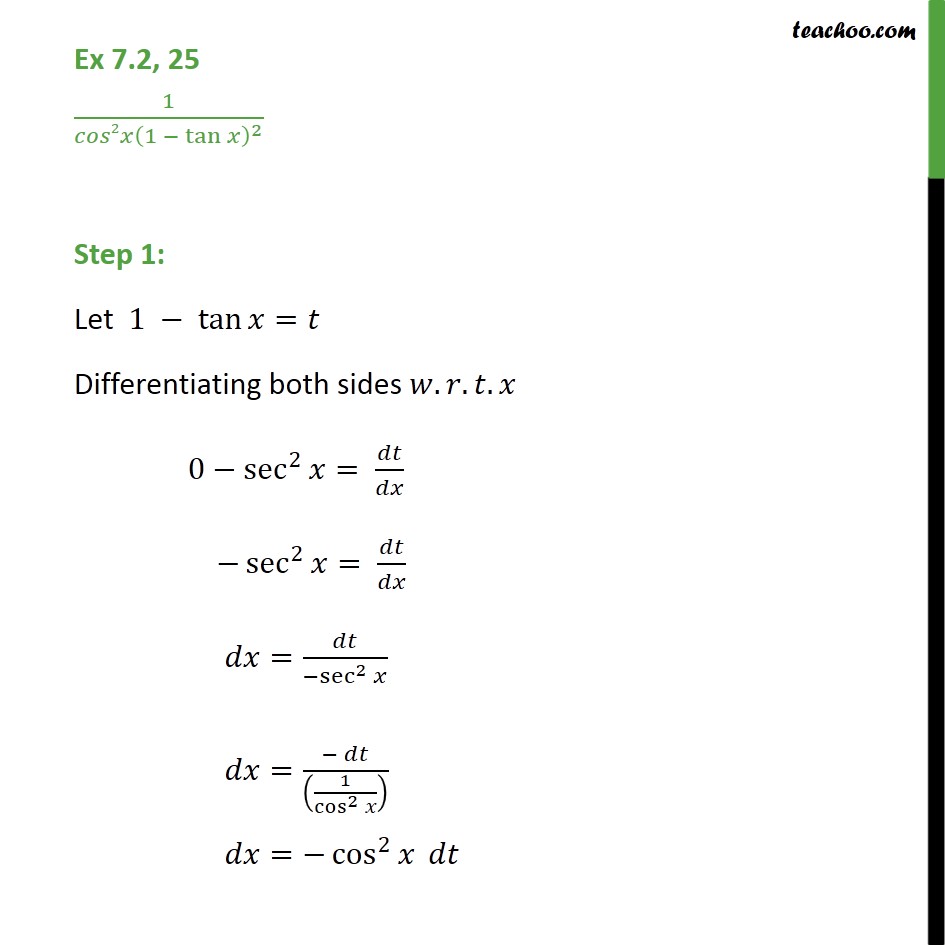



Ex 7 2 25 Integrate 1 Cos 2 X 1 Tan X 2 Ex 7 2




Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像
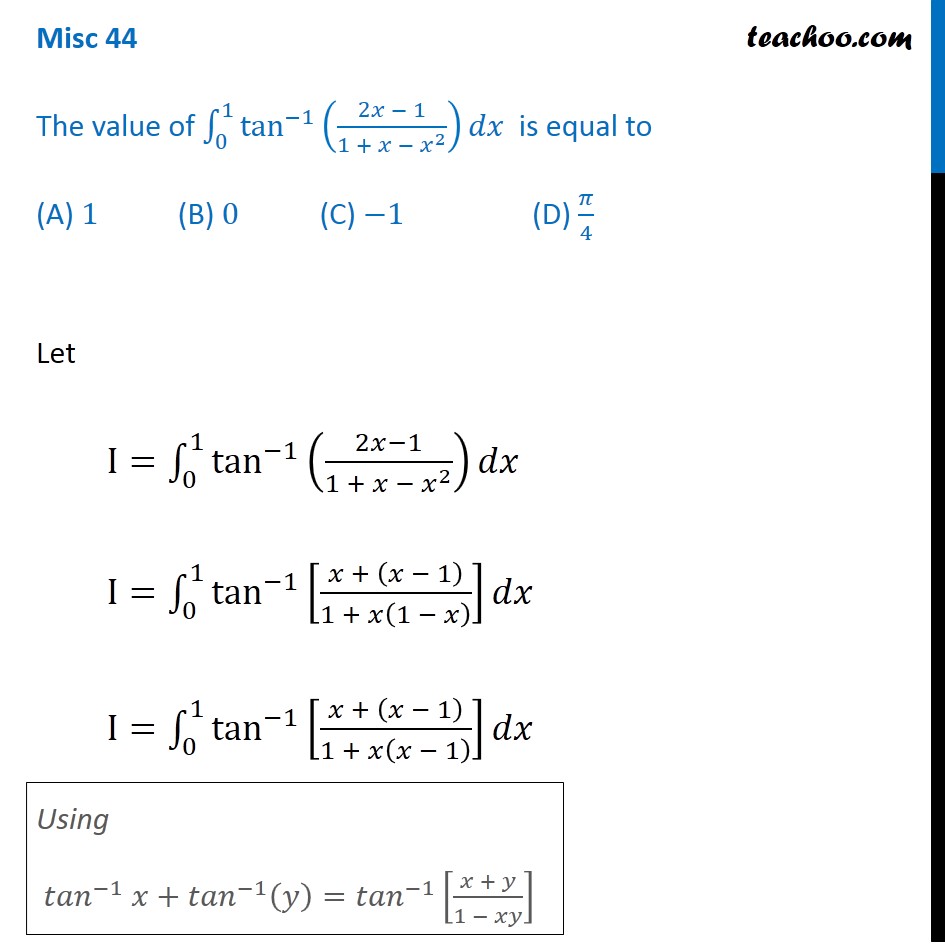
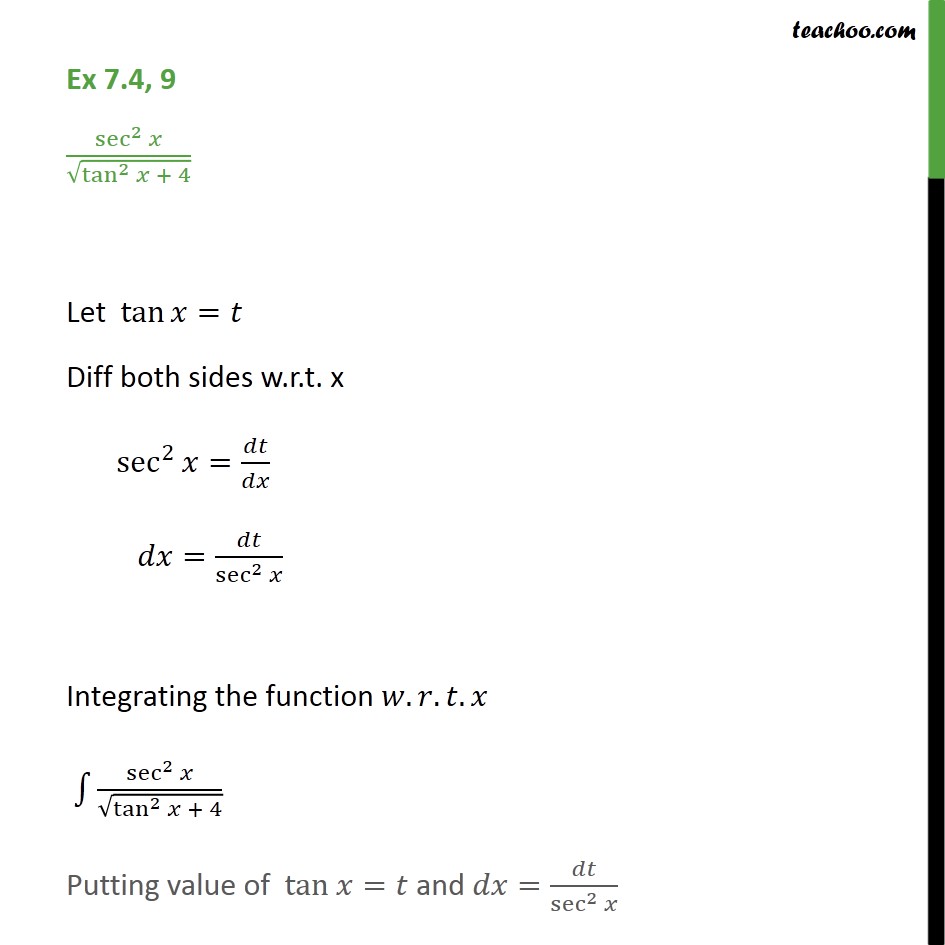
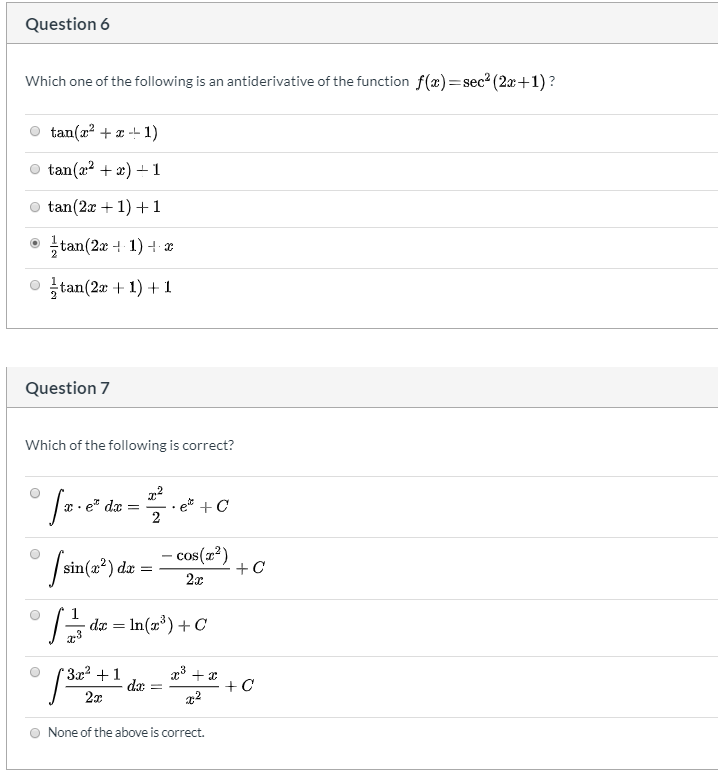
Since 4 4 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of 4 x 4 x with respect to x x is 4 d d x x 4 d d x x Move 4 4 to the left of sec 2 ( 4 x) sec 2 ( 4 x) Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that d d x x n d d x x n is n x n − 1 n x n 1 where n = 1 n = 1 Multiply 4 4 by 1 1\\int \tan^{2}x\sec{x} \, dx\ > Find The Antiderivatives Of The Following 1 Gauthmath The Integral Of Sec 4 X Tan X Mathematics Stack Exchange Integrate cot^2x To integrate cot^2x, also written as ∫cot 2 x dx, cot squared x, (cot x)^2, and cot^2 (x)we start by using standard trig identities to simplify the integral to a form we can work with We start with this standard and wellknown trig identity for cot 2 x We rearrange the Pythagorean for cos 2 x so that we can substitute itThis would normally be quite a difficult integral to solve However, the ever powerful trigonometric identities make this an easy problemIntroduction to Tan double angle formula let's look at trigonometric formulae also called as the double angle formulae having double angles Derive Double Angle Formulae for Tan 2 Theta \(Tan 2x =\frac{2tan x}{1tan^{2}x} \) let's recall the addition formula What Is The Integral Of Cos 2x Cos Square X 1 Free antiderivative calculator solve integrals with all the steps Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graph Integral of tan^2x, solution playlist page http//wwwblackpenredpencom/math/Calculushtmltrig integrals, trigonometric integrals, integral 0 yeah, you are going to have to use usubstitution twice I don't know if I am correct or not, but I changed everything to sin and cos before anything and manipulated it that way I then let u = cosx and du = sinx For the second usubstitution, I let v=u²1 and (1/2)dv = udu Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia What Is The Integration Of Tanx Tan2x Tan3x Dx Quora View this answer Since f is the antiderivative of the function tan2x x21, tan 2 x x 2 1, therefore {eq}\displaystyle f' (x) = \frac See full answer below(x^22x3)/ sqrt (x) dx Pay using PayPal (No PayPal account Required) or yourWe first recall that d dx tan(2x) = 1 cos2(2x) 2 = 2 cos2(2x); Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube 7 Techniques Of Integration Techniques Of Integration 7 Answer to Find an antiderivative of the function f(x) = sec^2 {2x} A 2tan 2x B 1/2(tan 2x) C 1/3 sec^3 (2x) D 1/6 (sec^3 (2x)) By signingFind the Integral sec(2x)tan(2x) Let Then , so Rewrite using and Tap for more steps Let Find Tap for more steps Differentiate Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set asCalculus questions and answers; تخته سفید Sect 5 5 23 Integral Of Sec 2x Tan 3x 1 Anytime you have to integrate an expression in the form a^2 x^2, you should think of trig substitution using tan θ Here's why If we have a right triangle with hypotenuse of length y and one side of length a, such that x^2 a^2 = y^2 where x is one side of the right triangle, a is the other side, and y is the hypotenuseIf you let u=tanx in integral (tan^2)x you get The general antiderivative of f(x) is F(x)C , where F is a differentiable function All that means is that if you differentiate the antiderivative, you get the original function so to find the antiderivative, you reverse the process of finding a derivative Misc 44 Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is Miscellaneous How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Youtube The antiderivative of sec(x) is equal to ln sec(x) tan(x) C, where C represents a constant This antiderivative, also known as an integral, can be solved by using the integration technique known as substitutionUse Subtitution tan xThis is very easy, and this involves the use of trig identities math\displaystyle \int \tan ^2\left(x\right)\,dx/math Since math\tan ^2\left(x\right)=1\sec ^2\left(x\right)/math, so we rewrite the equation as math Ex 7 2 21 Integrate Tan2 2x 3 Class 12 Cbse Ex 7 2 Intcos 1 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Dx Thanks for the A!A 2 tan 2x Find an antiderivative of the function f(x) = sec2 2x B 1 tan 2x C lsee 2x D Ise 2x Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculatorThe following is a list of integrals (antiderivative functions) of hyperbolic functionsFor a complete list of integral functions, see list of integrals In all formulas the constant a is assumed to be nonzero, and C denotes the constant of integration Mastering Olympiad Mathematics Putnam Definite Integral Hard Problem Evaluate Displaystyle Int 0 Frac Pi 2 Frac Dx 1 Tan X Sqrt 2 Int 1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2x Dx $$3\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx= tan^2x c$$ So simply divide by 3 to get your answer $$\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx= \frac{tan^2x}{3} \frac{c}{3}$$ Note that as $c$ is an real number we could replace $\frac{c}{3}$ with $c_2$ to write the answer more neatly as $$\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx= \frac{tan^2x}{3} c_2$$You get these gems as you gain rep from other members for making good contributions and giving helpful advice #2 Report 16 years ago #2 u = tanx du/dx = sec 2 x I = ∫ tan 4 x dx = ∫ tan 2 x tan 2 x dx = ∫ tan 2 x (sec 2 x 1) dxThe secant of x is 1 divided by the cosine of x sec x = 1 cos x , and the cosecant of x is defined to be 1 divided by the sine of x csc x = 1 sin x What S The Integral Of Int Tanx E X Dx Socratic Int Dx Sin 2x Tan 2x 2 Answers The answer is tanx−xc Click to see full answer Also know, what is the integral of tan 2 x?Dave's Math Tables Integral tan (x) ( Math Calculus Integrals Table Of tan x) Discussion of tan x = lncos x C 1 Proof Strategy Make in terms of sin's and cos's; The antiderivative of tan (x) can be expressed as either ln cos (x) C or as ln sec (x) C In these equations, C indicates a constant, ln is the natural logarithm function, cos indicates the function cosine and sec denotes the function secant Both solutions for the antiderivative of tan (x) can be found by using an integration technique What Is The Integral Of Tan X 2 Quora What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora Definition Antiderivative A function F is an antiderivative of the function f if F′ (x) = f(x) for all x in the domain of f Consider the function f(x) = 2x Knowing the power rule of differentiation, we conclude that F(x) = x2 is an antiderivative of f since F′ (x) = 2x2 Answers The answer is tanx−xc People Also Asked, what is the integral of tan 2 x?Proof of Integral of sec²x formula Take x as a variable, and it also represents angle of a right triangle According to trigonometry, the secant squared of angle x is written as sec 2 x in mathematical form The indefinite integration of secant squared function with respect to x is written mathematically as follows Integration Calculus 3 Ex 7 4 9 Integrate Sec 2 X Root Tan 2 X 4 Ncert Class 12 This would normally be quite a difficult integral to solve However, the ever powerful trigonometric identities make this an easy problemThis is a question which tests your knowledge of how to use trigonometric identities as well as integration As there is no way to immediately integrate tan^2(x) using well known trigonometric integrals and derivatives, it seems like a good idea would be writing tan^2(x) as sec^2(x) 1Find each antiderivative a ? Ppt Section 4 5 Integration By Substitution Powerpoint Presentation Id Calculus 7 2 22 Integral Of Tan 2x Sec 4x Youtube Integral Of Tan 2x Cot 2x 2 Calculus 1 Trig Integrals Calculus Mathematics Email Subject Lines Indefinite Integral Integral Of Tan 2 X Youtube How Do You Integrate Int Sec 1 X Tan 1 X Dx Socratic A N T I D E R I V A T I V E O F T A N 2 X Zonealarm Results Integral Of Secant Cubed Wikipedia Trigonometric Integrals Http Professormike Pbworks Com W File Fetch 7 2 Pdf Antiderivatives And Indefinite Integrals Video Khan Academy Solved Problem 6 To Find An Antiderivative Of F X Ta Chegg Com Integration By Parts Find The Derivative Of F X Integral 2tan X 0 2t 4 Chegg Com 1 Evaluate Sec 2 X 16 Tan 2 X Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community Finding The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com Integral 2 1 Integration 2x Tan 1 X2 1 X4 Dx Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Xboy9i11 7 Techniques Of Integration Techniques Of Integration As Ex 7 3 15 Integrate Tan3 2x Sec 2x Class 12 Ncert Ex 7 3 What Is Math Int Tan 2 2x Dx Math Quora Integral 2 Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia Integrate Tan 2x Integrate Tanx Tan 2x Tan3x Dx Maths Integrals Meritnation Com Solving The Integral Of Cos 2x Video Lesson Transcript Study Com Integrate Tan X Tan 2x Tan 3x Dx Maths Integrals Meritnation Com Integration With U Substitution The Integral Of Sqrt Tan 4x Sec 2 4x Math Videos Calculus Integrity Integral Of Tan X Video Khan Academy Integration Of Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Youtube Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia Reduction Formula For The Integral Of Tan N X Dx Steemit Integrate Cosec 2x The Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivativeit Integrals Of Hyperbolic Functions Web Formulas Integral Of 1 Tan 2 X Integral Example Youtube Finding The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com Evaluate The Integerals Int E Log 1 Tan 2 X Dx On Integrate Tanx Dx Studyrankersonline Integrate Tan 2x By Parts How To Evaluate Integrals Of Tan M X Sec N X Steemit Indefinite Integral Integration Calculus 2 Integral Of Sec 2 X Sqrt 1 Tan 2 X Using The Arcsine Function Math Videos Maths Exam Calculus Integration Of Inverse Tan 2x Integration By Parts Youtube How To Integrate 2x Sec 3 X 2 3 Tan X 2 3 Quora Ex 7 3 15 Integrate Tan3 2x Sec 2x Class 12 Ncert Ex 7 3 Integral Of Sec 6 X Tan 2 X Dx Evaluating The Integral Tan 2 X Tan 4 X Dx Youtube Powers Of Trigonometric Functions Integration Calculus 2 How To Integrate X Tan 2 X Dx Quora Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube Section 5 3 The Definite Integral Ppt Video Online Download How Do You Find The Antiderivative Of Int Sin 2xdx Socratic Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia Q45 Integral Of 1 Tan 2x Sec 2x Youtube Find The Most General Antiderivative Of Show All Work 2 6 3 2 Sec F X E Homeworklib Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia Integral Dx 1 Tan 2x Chegg Com Math Problems Simplifying With Trigonometry Identities And Then Integration Integral Of Tan2x Integration Of Tan2x Antiderivative Of Tan2x Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube Find The Antiderivatives Of The Following 1 Gauthmath Answered For The Function F X 2 Sec 2x Tan Bartleby Integrating Tan 2 2x Youtube How Do You Evaluate The Integral 1 Tan X 3 Sec 2 X Dx Within The Range 0 Pi 4 Socratic Solved Question 6 Which One Of The Following Is An Antide Chegg Com How To Integrate Tan 2x Youtube Logarithms Integral Of Natural Log Calculus How To Ex 7 2 21 Integrate Tan2 2x 3 Class 12 Cbse Ex 7 2




































































































































































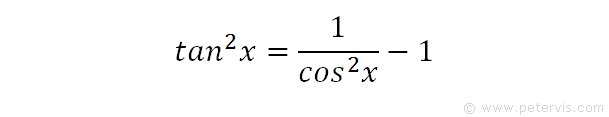























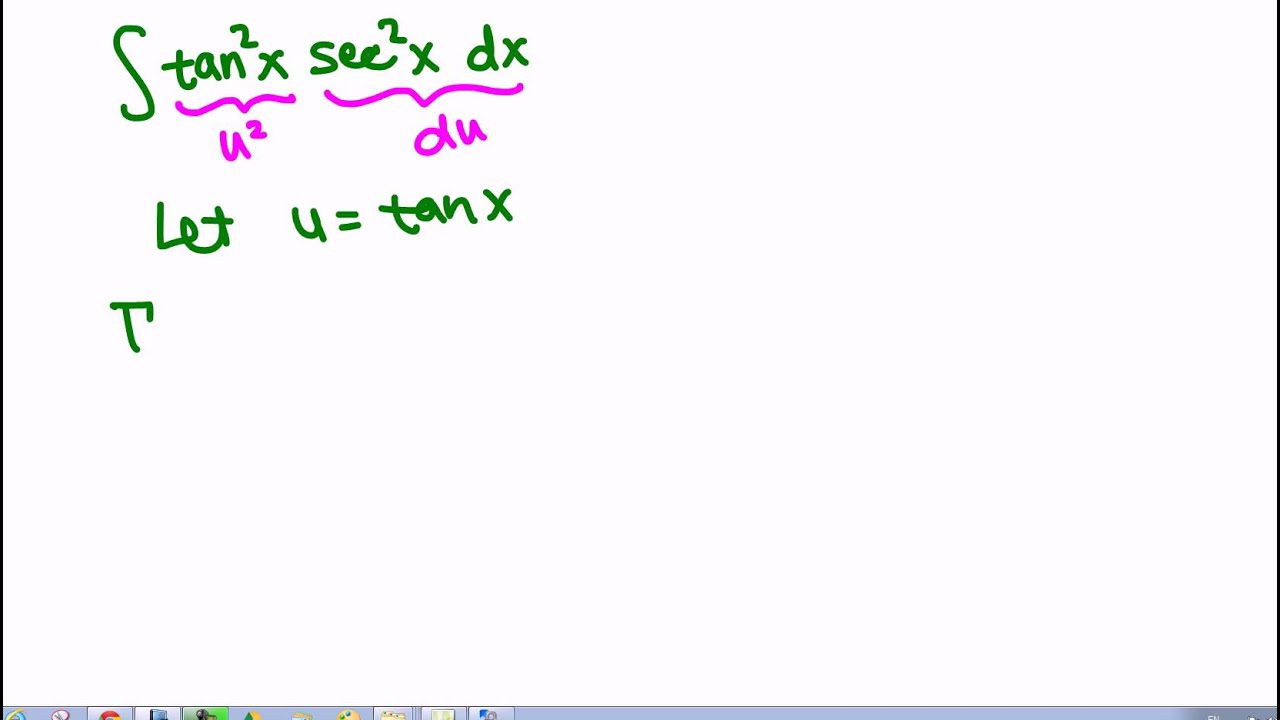







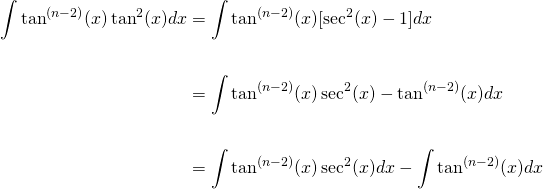














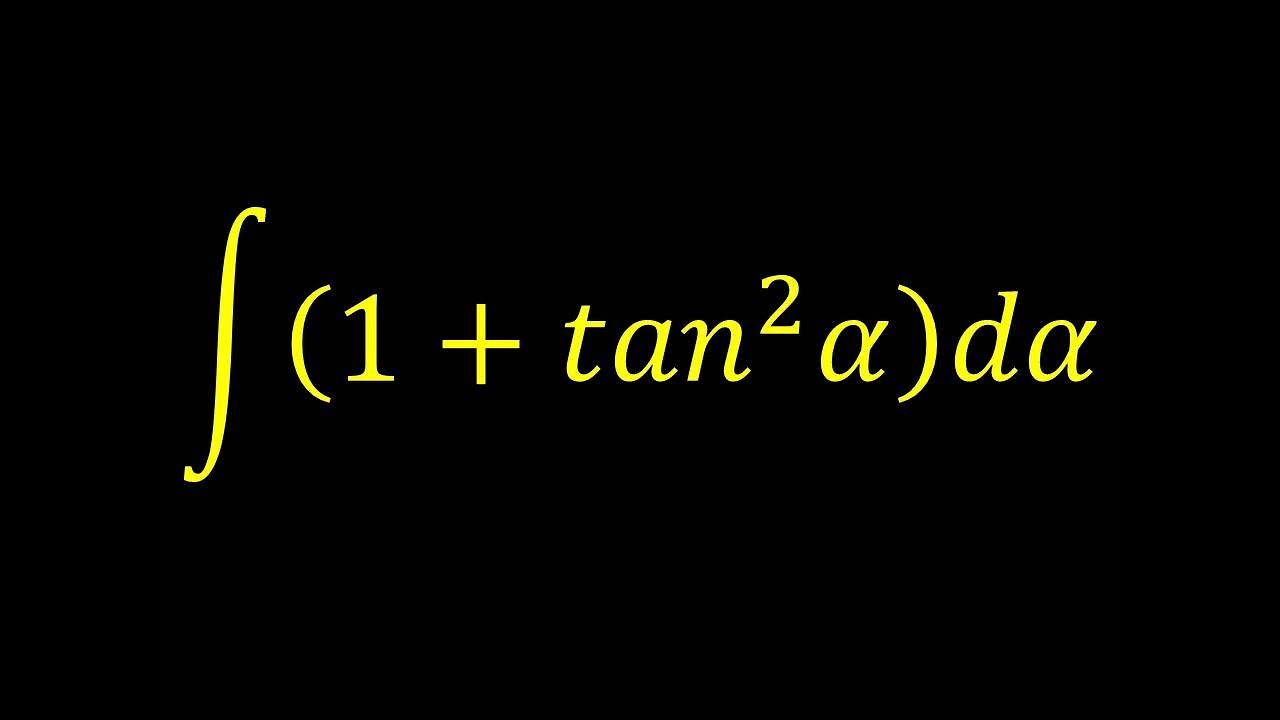







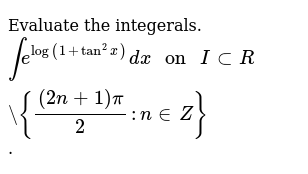

















































































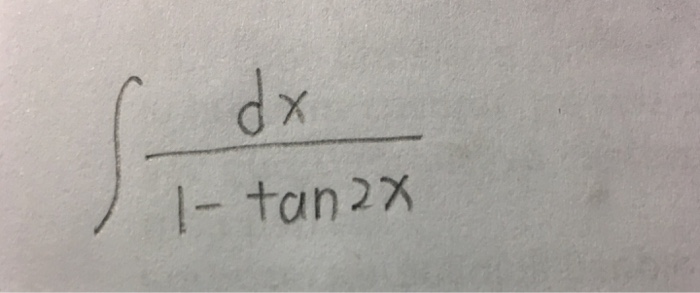














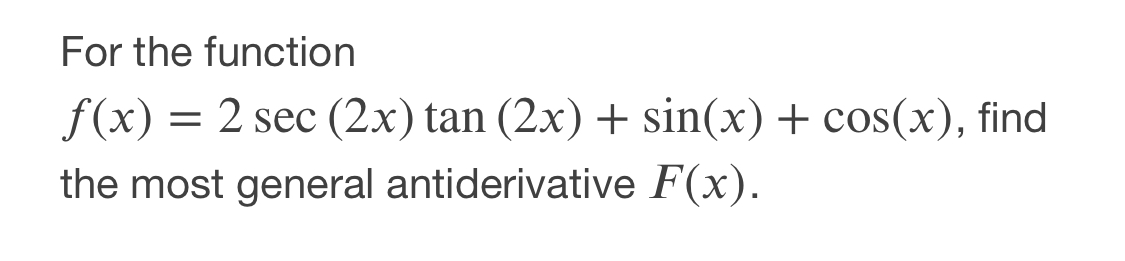



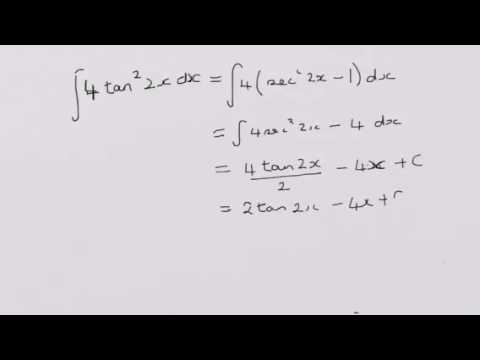
























0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿